All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
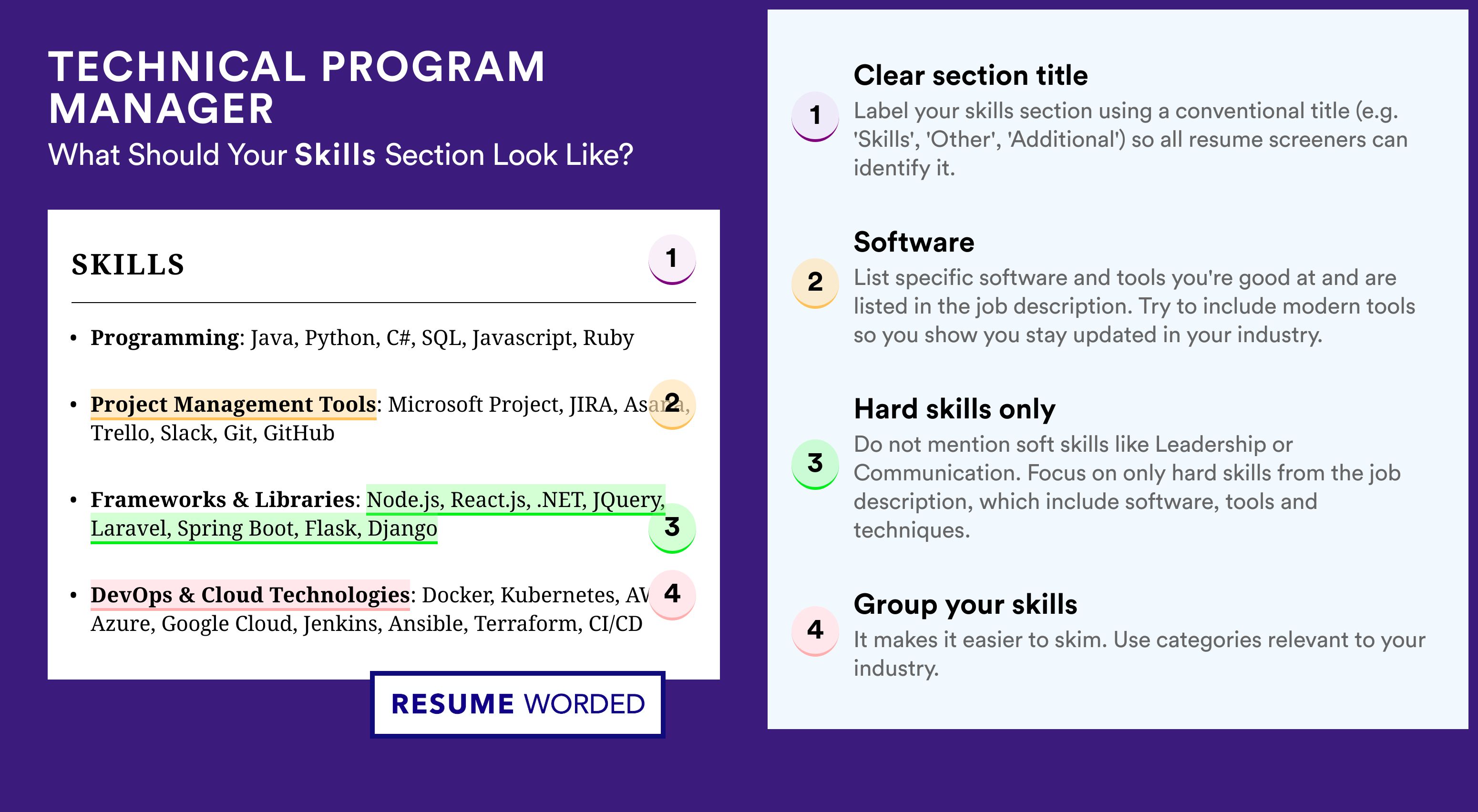
Connect these problems to relevant job teams, adhere to via till there's a service, and report the consumer resolution. Guarantee that all projects are following their spending plans and shipment times.
Establish a system to strategy, track, and document every solitary program you handle. Offer regular feedback to core groups, including the item group, design team, and development group. A bachelor's degree in computer system science or a relevant area is required. At the very least 4-6 years of experience in program management with IT projects is crucial.
Innovation is nitty-gritty when it comes to the innovation market, and within that standard, there's a behind the curtain orchestrator guaranteeing every little thing runs seamlesslythe Technical Program Supervisor (TPM). This unhonored hero plays a pivotal duty in the success of technology jobs, bringing order to turmoil and guaranteeing that the equipments of development turn smoothly.
What should I know before applying for a Program Management Certification For Tech job?
It's a delicate dancing in between establishing enthusiastic objectives and ensuring assumptions remain securely grounded actually - technical project manager certification. program management for tech companies. Yet it's not practically creating a strategy; it's concerning performing it perfectly. TPMs use the hats of both visionary planners and practical administrators, guaranteeing that every step aligns with the overarching project goals

In the vast landscape of technology tasks, effective interaction is the bridge that connects inconsonant groups and stakeholders. Below, TPMs beam as proficient translators, decoding the detailed language of technology for non-technical stakeholders. They bridge the void, making sure that everybody, no matter of their technological history, understands the project's goals and development.
They possess the insight to identify potential challenges, varying from unpredicted technical difficulties to external variables beyond the team's control. TPMs develop strategies to minimize risks, guaranteeing that the project sails via rainy weather condition with strength.
Below, TPMs tackle the role of allocators-in-chief, tactically distributing sources to optimize performance. From personnels to budgeting, they make certain that the job has the ideal people with the ideal skills and the necessary devices at every stage. Consistent analysis and adjustment are crucial. As the job landscape changes, TPMs reapportion sources dynamically, ensuring that the group continues to be dexterous and responsive.
What is the roadmap to becoming a Tech Program Manager Interview Prep?
TPMs, in this respect, come to be the gatekeepers of quality. They set strict criteria for every component of the project, from code to design, making sure that the end item fulfills or exceeds the specified standards.
TPMs produce a culture where quality is not simply an objective however a habit, permeating every aspect of the job. With their careful oversight, they infuse self-confidence in stakeholders and add to the long-term success and credibility of the company. Being an effective TPM calls for greater than just a propensity for task monitoring.
What does the hiring process for a Tpm Interview Prep look like?
While TPMs might not be coding wizards, they need a strong understanding of the technical landscape. This includes familiarity with the modern technologies involved, a recognition of market fads, and the capacity to understand the ramifications of technological choices. Leading without authority is a TPM's superpower. They need to influence and guide teams made up of individuals from numerous departments, each with their very own goals and priorities.
TPMs are the communication nexus of a job. Whether it's conveying complicated technical information to a non-technical audience or fostering cooperation among team participants, effective communication is non-negotiable.
Strategic assuming includes preparing for difficulties, picturing the job's trajectory, and aligning it with broader organizational objectives. As innovation develops, so does the role of the TPM. In recent times, the landscape has seen a change in emphasis from typical job monitoring to a much more vibrant and flexible method. Agile has become much more than simply a buzzword; it's a way of life for numerous TPMs.
, has actually come to be a cornerstone in the TPM's toolkit. In the age of large data, TPMs are increasingly depending on data-driven understandings to notify their decision-making procedures.
Is becoming a Technical Program Manager Courses worth it?

Unlike conventional project managers, TPMs need to deeply understand the technological aspects of the tasks they manage. This twin proficiency allows them to communicate with engineering groups successfully, comprehend technological difficulties, and ensure that tasks are finished on time and within budget. Whether you're aiming to work with a TPM or turn into one, comprehending the obligations and capability needed is essential for success in the tech industry.
The courses cover crucial subjects such as task lifecycle management, threat analysis, resource allotment, and software application development procedures. With a concentrate on real-world applications, our training ensures you are prepared to deal with the complexities of technical jobs in any industry. Gaining a certification can dramatically boost your profession prospects, showing to employers that you possess the expertise and skills needed to prosper in a TPM duty.
From start-ups to Fortune 500 firms, organizations around the world are looking for certified professionals to lead their technical programs. Whether you're seeking to hire a TPM or are interested in TPM tasks, TPM Institute can aid you browse the job market and connect you with the ideal possibilities. Our courses are not almost learning; they are regarding introducing your occupation in one of one of the most in-demand fields in the technology market.
Our are dedicated to offering you with the most effective possible education, using understandings based in real-world experience. They are devoted to helping you accomplish your qualification and do well in your career. For more details regarding our programs and qualifications, at Take the next action in your profession with TPM Institute and end up being a leader in technological program monitoring.
What interview questions should I expect as a Program Manager Vs Technical Project Manager?
There's a tendency for people to move towards extremes when conceptualizing technical program supervisors. For example, they're commonly referred to as either constantly taking part in coding or otherwise whatsoever. The reality is there is a range of technological depth among TPMs, and this oftentimes varies by task and client. Some projects require a leader with just sufficient technological depth to recognize modern technology style and compromises.
They can articulate complex technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders and facilitate cooperation in between varied teams. TPMs succeed at determining and settling problems that arise during project implementation, guaranteeing that jobs remain on schedule and within budget.
TPMs function to make certain that all team members are working in the direction of the very same goals, stopping miscommunication and lost effort. TPMs proactively address potential concerns, minimizing the chance of task hold-ups and failures.
TPMs work to guarantee that all team participants are functioning in the direction of the very same objectives, stopping miscommunication and lost effort. TPMs proactively address prospective concerns, reducing the chance of job delays and failings.
Latest Posts
The Best Websites For Practicing Data Science Interview Questions
Best Free Github Repositories For Coding Interview Prep
Best Resources To Practice Software Engineer Interview Questions